


NASAL AERODYNAMICS and RHINOSINUSITISES
PRIMARY VALVE OF THE NOSE - IT'S HIS CAVERNOUS BODIES
Relationship between two parallel respiratory structures in the nose
The main cause of the night snoring is violations of the nasal aerodynamics
The functionality of the small ostiums of the nasal sinuses
Critical comparison of opposite opinions about the function of the nasal sinuses using Occam's Razor
The real significance of the limen nasi
VARIANTS OF NASAL AERODYNAMICS
NORMOGRAM OF NASAL AERODYNAMICS
PHYSIOLOGICAL BRIDGE REPRESENTED BY THE NASAL VALUE
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF NASAL AERODYNAMICS
SEPTOPLASRY UNDER CONTROL OF NASAL AERODYNAMICS
CONTRAINDICATION TO SEPTOPLASTY
PROTECTION OF THE INFERIOR NASAL PASSAGE FROM INSPIRATION
THE INSIDIOUSNESS OF THE UNILATERAL "SOUTHERN" NASAL AERODYNAMICS.
SNORING WHEN NASAL RESPIRATION IS SAVED.

In the given textbook, with the help of the author's technique was the first to research airflows in nasal passages, that has allowed to conduct the deep pathophysiological analysis of features nasal aerodynamics, which plays a leading role in the development of seasonal ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISEASE (ARD), with stagnant sinusitises, by the way RHINOSINUSITISES (RS).
The proposed rapid method of determining violations of a nasal aerodynamics considerably accelerates their diagnostics, facilitates the selection of pathogenetic therapy and helps develop pathogenesis-based preventive care (prophylaxis).
Designed as therapeutic ways of seasonal protection from violations of nasal aerodynamics and surgical ways of renovation of protective properties of aerodynamics of a nose, the application which one allows more successfully to treat and to notify seasonal ARD with RS.
The new techniques are protected by the Russian patents.
2. Basic protection from of the seasonal ARD with RS is the mucociliary protective mechanism of nasal mucous membrane, which consists of the mucociliary transport on helium film and the mucociliary clearance beneath the helium film, which successfully complement each other ;
3. The protective properties of nasal aerodynamics are playing a leading role among the nasal protective mechanisms that aim to preserve the activity of the mucociliary protective mechanism;
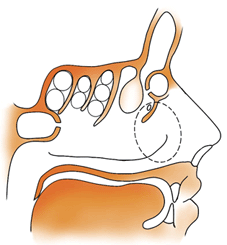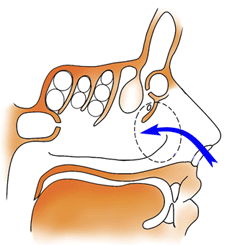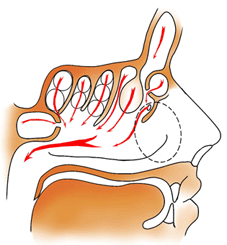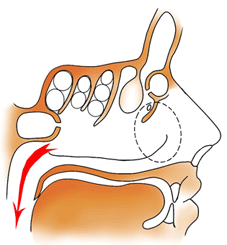
4. The nasal aerodynamics consists of two parallel respiratory structures, as form of the middle and superior nasal passages together with nasal sinuses, which perform the basic respiratory and protective function of the nose, and inferior nasal passage together with common nasal passage, which perform the reserve respiratory functions, that is activated when the bandwidth of the basic respiratory nasal airways is not enought for nasal respiration;
5. When the main air stream passes through the basic respiratory nasal airways (nasal sinuses), the air is warming to plus 25oC even at minus 20oC outside, that successfully protects against seasonal ARD with the RS and therefore, such type of the nasal aerodynamics is regarded as the Northern Variant of the nasal Aerodynamics (NVA), which corresponds normogramme of nasal aerodynamic;
6. A distinctive feature of the NVA is a distance between the anterior end of the inferior turbinate and the nasal septum within 2 mm and therefore an air column in the gleam of such width in fact blocking the inferior nasal passage and directs the main air flow in the middle and superior nasal passages with nasal sinuses, actually performing the role of “physiological jumper”;
7. When the main air stream passes through the reserve respiratory nasal airways, during cold temperature season the inferior nasal passage and nasopharynx on so much cool, that programming seasonal ADR, so such variant of the nasal aerodynamics is more suitable to a warm climate of Southern latitudes, due to the what he regarded as the Southern Version of nasal Aerodynamics (SVA);
8. The distinctive feature of SVA is not only the width of a lumen more than 2 mm between the anterior end of the inferior turbinate and the nasal septum, which leading to seasonal ARD, but also stagnant inflammatory process in the middle and superior nasal passages with the nasal sinuses, forming stagnant RS which is manifested in the form of seasonal ARD with the RS;
9. Overlapping of the reserve respiratory nasal airways programmed with the help of the physiological oedema his cavernous bodies, especially during sleep that is directing the main air stream of the nose passes through the nasal sinuses, in order to acieve maximum protective properties of a nose during sleep from ARD, but when a person is awake the bandwidth of the main nasal respiratory way becomes not enough, physiological oedema is receding and opening the reserve respiratory nasal airways that no longer threatens the ARD development due to sufficient activation the protective properties of the waking organism;
10. Additional overlap of the inferior nasal passage with the help of the limen nasi, anterior synechiae, spikes and curvatures of the nasal septum, promote the diversion of the main nasal air flow in the middle and superior nasal passages with nasal sinuses which activates the protective properties of the nasal aerodynamics;
11. Exceptionally only small ostiums of the nasal cellular system and nasal sinuses, working like a spray mechanism of the H.L.Bergson (1859–1941), provide their extremely active ventilation;
12. The protective properties of the nasal aerodynamics is also evident during expiration when warm and moist air stream helps to restore the nasal mucous membrane injured during inspiration, especially for the SVA ;
13. The unilateral SVA is the most aggressive, because it leads to a double overload of the inferior nasal passage, which working for both halves of the nose, that is typical for a deviated septum, so during septoplasty the NVA reconstruction from the SVA is needed;
14. Pathogenetic therapy of seasonal ARD with the RS in SVA, should be directed as at the treatment of acute post-traumatic inflammation of the reserve nasal respiratory airways, as well at the treatment of stagnant chronic inflammation in the middle and superior nasal passages with nasal sinuses;
15. Methods of therapeutic protection from violations of the SVA as well as surgical reconstruction of the NVA from of the SVA should be recognized as pathogenetic grounded prophylaxis of the seasonal ARD with the RS;
16. Since the main cause of the night snoring is blocking of the reserve respiratory nasal airway at SVA because of chronic congestive MS, physiological edema cavernous bodies and protective rhinedema of the inferior nasal passage, which leads to the mouth breathing, pathogenetic treatments snoring during sleep should be recognized as forced airing sinuses or surgical reconstruction the NVA from the SVA.
 |
The real significance of the limen nasiUlyanov Y.P., Sadyev H.D., Sadyev T.H. |
|
|

